
(eds) (2009), Parsing the Turing Test: Philosophical and Methodological Issues in the Quest for the Thinking Computer, Springer Publishing Company. View in Google ScholarĮpstein R., Roberts G., Beber G. The inside story of Artificial Intelligence and our race to build the future, WH-Alley, London. (1996), “Assessing Agreement on Classification Tasks: The Kappa Statistic, ”Computational Linguistics 22 (2): 249–254. Osherson, (eds), The MIT Press, London: 377–425. (1995), “The mind as the software of the brain,” An Invitation to Cognitive Science – Thinking, E. (2003), “CAPTCHA: Using Hard AI Problems For Security,” Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2656: 294–311. However, this may not truly indicate emotional intelligence or awareness it may simply mean the computer had a highly relevant and competent set of code.Ahn L., Blum M., Hopper N.J., Langford J. For example, a computer may successfully fool an interrogator based on its ability to process responses similarly as a human.


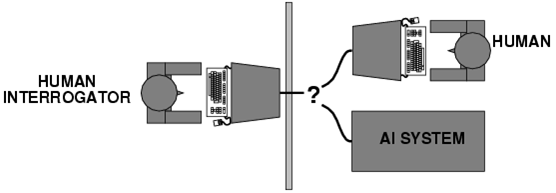
There are variations to the Turing test as well as modifications to the approach of asking questions in different AI tests.Not everyone accepts the validity of the Turing Test, but passing it remains a major challenge to developers of artificial intelligence.According to the test, a computer program can think if its responses can fool a human into believing it, too, is human.The Turing Test measures the intelligence of a test subject to determine whether a machine can demonstrate intelligence.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
